Overview
The following diagram provides a high-level overview of the system architecture:
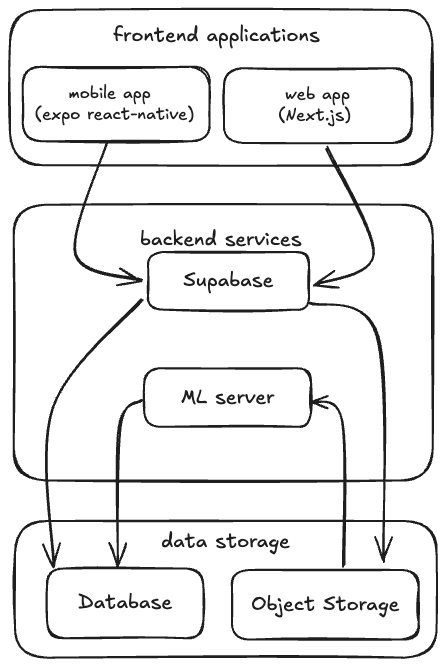
Frontend Applications
The system consists of two frontend applications serving different purposes:
Mobile App
The mobile app focuses on servicing contributors and is responsible for:
- User registration
- Data aggregation
- Displaying device-specific information
Web App
The web app caters to data-set users and is responsible for:
- Displaying data-sets
- Facilitating transactions
Backend Services
The backend services are deployed on their own infrastructure and consist of:
Supabase
Supabase, an open-source alternative to Firebase, provides a suite of backend services for building applications. In the mobile app, it serves as a managed backend platform handling:
- Database: PostgreSQL database for storing and querying data
- Authentication: User signup, login, and session management
- Real-time subscriptions: Live data updates to clients
- Storage: S3 compatible file storage and management
- Edge Functions: Serverless functions for custom backend logic (minimally used in this case)
- Auto-generated APIs: REST and GraphQL APIs based on the database schema
Unsorted AI heavily relies on PostgreSQL Row Level Security (RLS) access policies. These policies, written in SQL, enforce who can create, read, update, or delete data from the database. RLS is also used for S3 storage.
Machine Learning Server
More context needed to comprehensively explain the ML server use case.
Data Storage and Processing
The system handles terabytes of structured and unstructured data daily, requiring specific actions. User devices push data to object storage via resumable uploads, including metadata describing the data and its origin. The machine learning server ingests the data, sorts it, records it in the PostgreSQL database, and moves it to a data set bucket in object storage.
This process is crucial for:
- Rewarding users for their data contribution
- Creating datasets ready for AI model training
Data Flow
- User devices collect data and push it to object storage via the mobile app.
- The machine learning server ingests the data from object storage.
- The machine learning server sorts and records the data in the PostgreSQL database.
- The machine learning server moves the processed data to a data set bucket in object storage.
- The web app retrieves data-sets from the data set bucket for display and transaction facilitation.
- The mobile app communicates with Supabase for user registration, authentication, and real-time updates.
- Supabase enforces data access control through PostgreSQL Row Level Security (RLS) policies.